
Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial and hospital settings. The biofilm mode of growth protects the colonizing bacteria and enables them to withstand host immune responses and exhibit high tolerance to treatment with the highest deliverable doses of antibiotics. Hence, the development of novel therapeutics to the treatment of biofilm is urgently needed. One particularly notorious biofilm former that is known to cause infections on medically implanted foreign bodies is Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa).
Quorum sensing (QS) is a system of stimulus and response correlated to population density. P. aeruginosa uses cell-to-cell communication or QS to control the production and secretion of virulence factors, which, deployed at the right time and place, enables evasion of the host defenses. QS inhibitors offer a potential solution to the deficiencies associated with use of traditional antibiotics to treat infections caused by bacterial biofilms and multidrug-resistant bacteria.
A research group led by Dr. ZHANG Lixin at the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMCAS) and his collaborator Dr. WANG Yuqiang at Jinan University College of Pharmacy developed a high-throughput synergy screening platform to explore the full potential of natural products. Following a large-scale screening of their library, 14-Alpha-lipoyl andrographolide (AL-1) was found to be one of the best biofilm inhibitors.
AL-1 inhibited the production of the exopolysaccharide, pyocyanin components and the flagella function without affecting its growth. Docking study showed that AL-1 can interact with LasR. Then AHL-deficient derivative stain was used to test the effects of AL-1 on las system.
The result demonstrated that AL-1 interfered with the las system via inhibiting LasR-3-oxo-C12-HSL interaction. The expression of Las and Rhl genes was reduced in the presence of AL-1. AL-1 had effect on Psl both at transcriptional and translational level (Figure) and it sensitized the bacterium P. aeruginosa PAO1 to a variety of antibiotics for distinct synergistic effects. It showed that biofilm formation, the production of the exopolysaccharide and pyocyanin were completely inhibited when AL-1 combined with AZM, CIP, and STR.
This study has been published online in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.
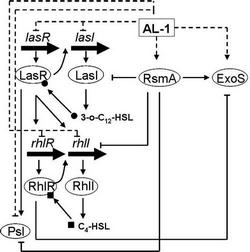
Proposed model of the effect of AL-1 on QS related genes and Type III secretion system effector exoS, dash lines indicate the effects of AL-1, solid lines indicate the QSnetwork. Arrow heads, activation, flat arrow heads, repression. (Image by ZHANG Lixin et al)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

